Scientists explore how dinosaurs fed and coexisted
Researchers at the University of Bristol and the Natural History Museum, London, are investigating how the largest animals ever to have walked the earth fed, and how this allowed them to live together.
Saurapods dominated the land between 210 and 65 million years ago. With the largest weighing 80 tonnes (more than 11 elephants), they are the most colossal land mammals of all time and would have required huge amounts of food. Yet multiple sauropod species often lived side by side. For example, more than 10 species of sauropod are known from the Late Jurassic Morrison Formation in the US.
Together with the Natural History Museum, David Button, a PhD student in Bristol's School of Earth Sciences, explored how so many giant herbivores could have coexisted - particularly when it is considered that the semi-arid environment of the Morrison Formation would have limited plant growth.
Focusing on the skull and jaws of sauropods, the team used a variety of biomechanical techniques to determine how they functioned.
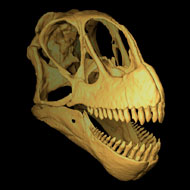
Digital reconstructions of the skulls of two sauropods - Camarasaurus and Diplodocus - were built using CT scans, including the jaw and neck muscles. These were recreated using traces left on the bones where the muscles would have been attached.
Scientists used this data to create a biomechanical computer model of the skull of Camarasaurus. By comparing the model to one of Diplodocus, they were able to find out how the dinosaurs fed.
Mr Button said: "Our results show that although neither could chew, the skulls of both dinosaurs were sophisticated cropping tools. Camarasaurus had a robust skull and strong bite, which would have allowed it to feed on tough leaves and branches.
"Meanwhile, the weaker bite and more delicate skull of Diplodocus would have restricted it to softer foods like ferns. However, Diplodocus could also have used its strong neck muscles to help it detach plant material through movements of the head. This indicates differences in diet between the two dinosaurs, which would have allowed them to coexist.”
The team also found that other sauropods from the Morrison Formation had highly varied feeding adaptions, suggesting they may have had different diets.
The research paper is published in Proceedings of the Royal Society B.
Image © Mr. David J. Button



 The latest
The latest