New map shows patterns in zoonotic diseases
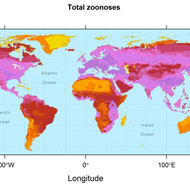
Research to assemble a map illustrating records of mammal-to-human disease outbreaks has revealed understudied patterns.
Researchers at the Carys Institute of Ecosystem Studies and the University of Georgia used data on all 27 orders of terrestrial mammals to track and record where outbreaks have and therefore are more likely to occur.
Previously believed to be inherently unpredictable, outbreaks of zoonoses appear to occur in unlikely hotspots.
Disease ecologist and first author Barbara Han said: “I was rather surprised to see that hotspots of zoonotic diseases didn’t match hotspots of biodiversity more closely”.
Areas of high species diversity, such as the tropics, with a more zoonotic host species did not have correlating levels of zoonotic diseases.
Han continued: “In contrast, more of the species living in the northern latitudes, such as the Arctic Circle, carry more zoonoses. Understanding the implications of this pattern in light of climate warming trends will be an important line of enquiry”.
Using information from the Global Infectious Disease and Epidemiology Network database and other sources, the map may help eventually to prepare for and predict further outbreaks of zoonoses and subsequent transmission to humans.
“Understanding where animals are distributed and why may not seem applicable to our day-to-day lives” Hans says, but the big breakthroughs that we need as a society rely exactly on this kind of basic scientific knowledge”.
Image (C) Drew Kramer



 The latest
The latest